728x90
❤️ 배운 것
Boxplot
IQR = Q3- Q1
inter quartile range
whis => default 1.5
위스커(박스플랏의 수염: 위아래) 바깥의 점은 outlier
def box_plot_test():
n_student = 100
math_scores = np.random.normal(loc=50, scale=10, size=(100,))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7))
ax.boxplot(math_scores)
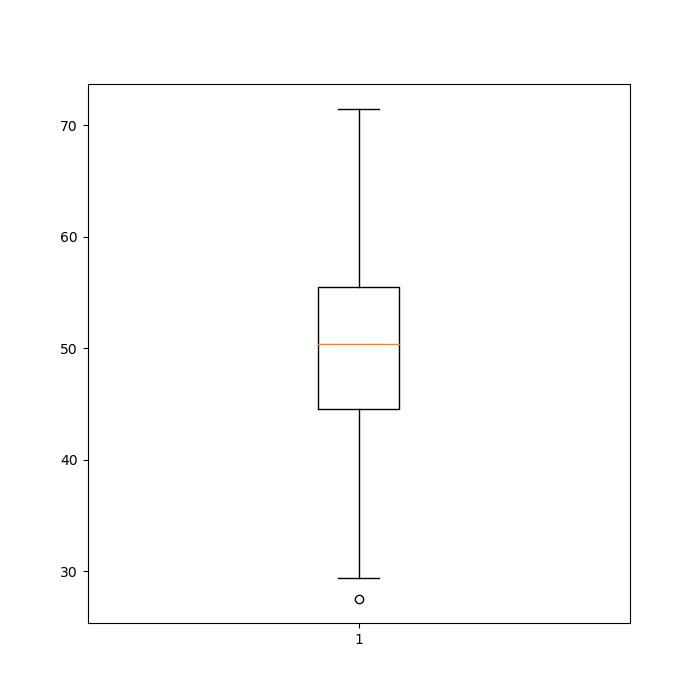
showfliers -> outlier 보여줄지 여부
vert -> false면 수평으로 보여주기
mean: 평균
median: 중앙값
median_props는 중앙값 보여주는 설정
k: black, b: blue
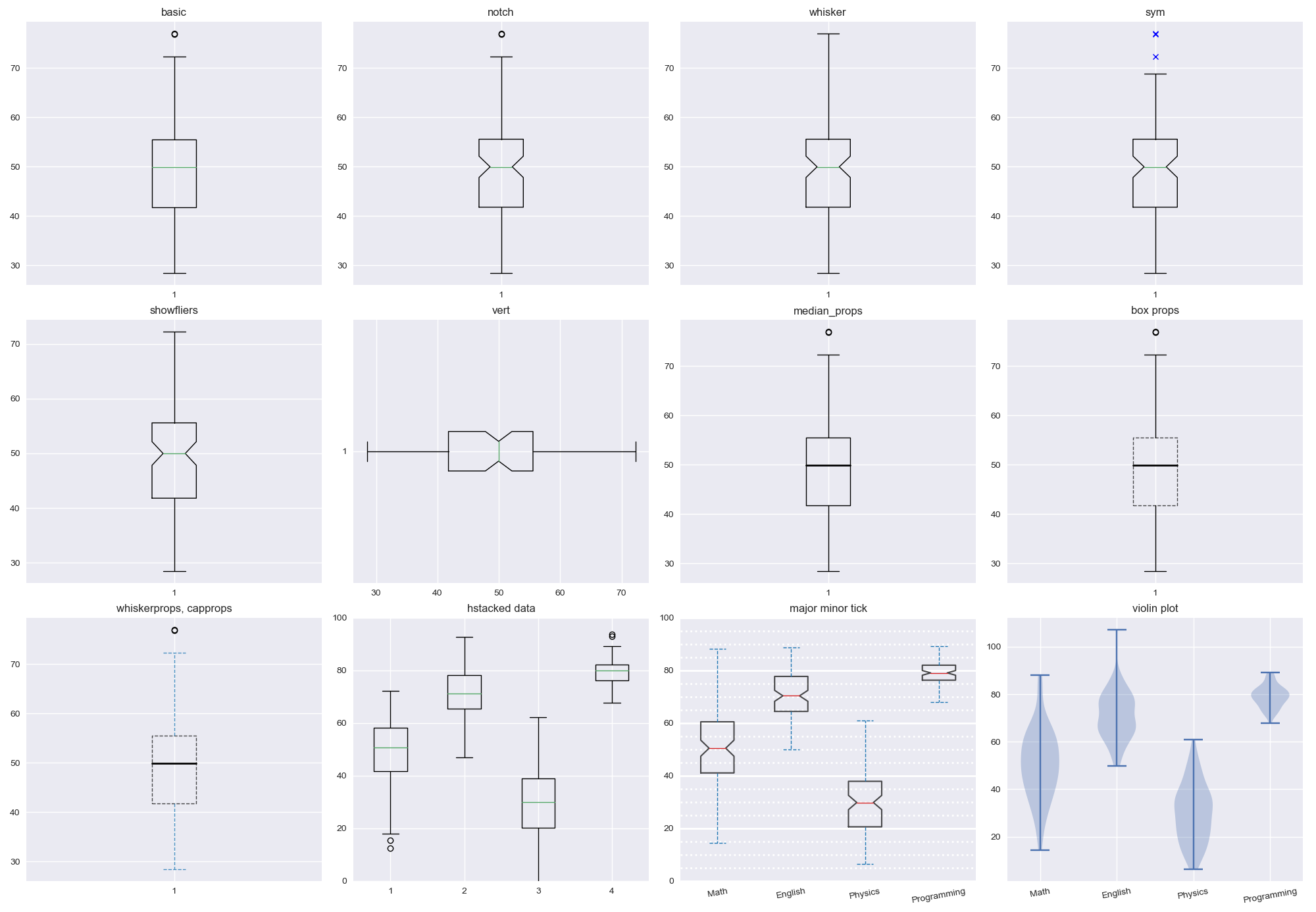
Box plot variation
def box_plot_test():
n_student = 100
math_scores = np.random.normal(loc=50, scale=10, size=(100,))
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=4, figsize=(20, 15))
# axes = axes.flatten()
''' basics '''
axes[0, 0].set_title('basic')
axes[0, 0].boxplot(math_scores)
axes[0, 1].set_title('notch')
axes[0, 1].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True)
axes[0, 2].set_title('whisker')
axes[0, 2].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True, whis=2)
axes[0, 3].set_title('sym')
axes[0, 3].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True, whis=1, sym='bx')
'''showfliers, vert, median props'''
axes[1, 0].set_title('showfliers')
axes[1, 0].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True, showfliers=False)
axes[1, 1].set_title('vert')
axes[1, 1].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True, showfliers=False, vert=False)
median_props = {'linewidth': 2, 'color': 'k'}
axes[1, 2].set_title('median_props')
axes[1, 2].boxplot(math_scores, medianprops=median_props)
box_props = {'linestyle': '--', 'color': 'k', 'alpha': 0.7}
axes[1, 3].set_title("box props")
axes[1, 3].boxplot(math_scores, medianprops=median_props, boxprops=box_props)
whisker_props = {'linestyle': '--', 'color': 'tab:blue', 'alpha': 0.8}
axes[2, 0].set_title("whiskerprops, capprops")
axes[2, 0].boxplot(math_scores, medianprops=median_props, boxprops=box_props,
whiskerprops=whisker_props, capprops=whisker_props)
''' hstacked data '''
n_student = 100
math_scores = np.random.normal(loc=50, scale=15, size=(100, 1))
chem_scores = np.random.normal(loc=70, scale=10, size=(n_student, 1))
phy_scores = np.random.normal(loc=30, scale=12, size=(n_student, 1))
pro_scores = np.random.normal(loc=80, scale=5, size=(n_student, 1))
data = np.hstack((math_scores, chem_scores, phy_scores, pro_scores))
axes[2, 1].set_ylim([0, 100])
axes[2, 1].set_title("hstacked data")
axes[2, 1].boxplot(data)
''' major minor tick '''
axes[2, 2].set_title("major minor tick")
# n_student = 100
math_scores = np.random.normal(loc=50, scale=15, size=(100, 1))
english_scores = np.random.normal(loc=70, scale=10, size=(100, 1))
physics_scores = np.random.normal(loc=30, scale=12, size=(100, 1))
programming_scores = np.random.normal(loc=80, scale=5, size=(100, 1))
data = np.hstack((math_scores, english_scores, physics_scores, programming_scores))
median_props2 = {'linewidth': 1, 'color': 'tab:red'}
box_props2 = {'linewidth': 1.5, 'color': 'k', 'alpha': 0.7}
whisker_props2 = {'linestyle': '--', 'color': 'tab:blue'}
# labels
labels = ['Math', 'English', 'Physics', 'Programming']
axes[2, 2].set_xticklabels(labels)
# axes[2, 2].tick_params(labelsize=20)
axes[2, 2].tick_params(axis='x', rotation=10)
axes[2, 2].boxplot(data, labels=labels,
notch=True, medianprops=median_props2, boxprops=box_props2,
whiskerprops=whisker_props2, capprops=whisker_props2)
axes[2, 2].set_ylim([0, 100])
major_yticks = np.arange(0, 101, 20)
minor_yticks = np.arange(0, 101, 5)
axes[2, 2].set_yticks(major_yticks)
axes[2, 2].set_yticks(minor_yticks, minor=True)
axes[2, 2].grid(axis='y', linewidth=2)
axes[2, 2].grid(axis='y', which='minor', linewidth=2, linestyle=':')
axes[2, 2].grid(axis='x', linewidth=0)
''' violin plot '''
n_group = np.arange(len(labels))
axes[2, 3].set_title("violin plot")
axes[2, 3].violinplot(data, positions=n_group)
axes[2, 3].set_xticks(n_group)
axes[2, 3].set_xticklabels(labels)
axes[2, 3].tick_params(axis='x', rotation=10)
# axes[2, 2].tick_params(labelsize=20, bottom=False, labelbottom=False) # 라벨 지우기
# fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.1) # horizontal space(위아래)를 10%로 줄이는 것
Numpy
ndarray 기본 생성 방법
vec_np = np.array([1, 2, 3]) np.array() 안에 list를 넣으면 ndarray가 생성됨
np.full((2, 2), np.inf)
array([[inf, inf],
[inf, inf]])
>>> np.full((2, 2), 10)
array([[10, 10],
[10, 10]])- np.inf = $\infty$
arange
np.arange(10)
Out[8]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
np.arange(2, 5)
Out[9]: array([2 3 4])
np.arange(2, 10, 2)
Out[10]: array([2, 4, 6, 8])
np.arange(1.5, 10.5)
Out[11]: array([1.5, 2.5, 3.5, 4.5, 5.5, 6.5, 7.5, 8.5, 9.5])
np.arange(1.5, 10.5, 2.5)
Out[12]: array([1.5, 4. , 6.5, 9. ])- np.arange는 1:시작, 2:끝, 3:스텝(구간)으로 생성
linspace
np.linspace(0, 1, 5)
Out[13]: array([0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. ])
np.linspace(0, 1, 10)
Out[14]:
array([0. , 0.11111111, 0.22222222, 0.33333333, 0.44444444,
0.55555556, 0.66666667, 0.77777778, 0.88888889, 1. ])- np.linspace는 1:시작, 2:끝, 3:개수로 생성
randn
random_values = np.random.randn(300)
'''
[0. 0.11111111 0.22222222 0.33333333 0.44444444 0.55555556
0.66666667 0.77777778 0.88888889 1. ]
(300,)
'''np.random.normal
normal = np.random.normal(loc=[-2, 0, 3],
scale=[1, 2, 5],
size=(200, 3))- 200 x 3 크기의 정규분포에서 랜덤 선택한 값 3묶음
단일 평균, 표준편차로 nxn 추출
normal = np.random.normal(loc=-2, scale=1, size=(3, 3))
print(normal)
'''
[[-0.21198265 -2.51857286 -2.0761132 ]
[-2.16084686 -1.50902093 -1.63418275]
[-1.80634427 -2.61567043 -2.04913825]]
'''randn vs rand
random_values = np.random.randn(300)
uniform = np.random.rand(1000)- randn : 표준정규분포로 평균 0 분산 1 기준으로 300개 추출
- rand : uniform 무작위로 0~1 사이 값 1000개 추출
normal vs uniform
normal = np.random.normal(loc=[-2, 0, 3],
scale=[1, 2, 5],
size=(200, 3))
uniform = np.random.uniform(low=-10, high=10, size=(10000, ))- normal : 정규분포로 평균, 분산을 정해서 200개 추출
- uniform : 무작위로 low ~ high 사이 값 10000개 추출
randint
randint = np.random.randint(low=0, high=7, size=(20,))- randint : low에서 high 사이의 정수 20개 추출
size
M = np.ones(shape=(10,))
N = np.ones(shape=(3, 4))
O = np.ones(shape=(3, 4, 5))
P = np.ones(shape=(2, 3, 4, 5, 6))
print("size of M: ", M.size) # size of M: 10
print("size of N: ", N.size) # size of N: 12
print("size of O: ", O.size) # size of O: 60
print("size of P: ", P.size) # size of P: 720- size : 원소의 개수
reshape
a = np.arange(6)
b = np.reshape(a, (2, 3))
print("original ndarray: \n", a)
print("reshaped ndarray: \n", b)
'''
original ndarray:
[0 1 2 3 4 5]
reshaped ndarray:
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]]
'''
a = np.arange(24)
b = np.reshape(a, (2, 3, 4))
print("original ndarray: \n", a)
print("reshaped ndarray: \n", b)
'''
original ndarray:
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23]
reshaped ndarray:
[[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[[12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23]]]
'''
a = np.arange(12)
b = a.reshape((2, -1))
c = a.reshape((3, -1))
d = a.reshape((4, -1))
e = a.reshape((6, -1))
print(b.shape, c.shape, d.shape, e.shape)
''' (2, 6) (3, 4) (4, 3) (6, 2) '''
a = np.random.randint(0, 10, size=(2, 2))
print(a)
'''
[[8 2]
[0 5]]
'''
row_vector = a.reshape(1, -1)
col_vector = a.reshape(-1, 1)
print(row_vector.shape, col_vector.shape)
''' (1, 4) (4, 1) '''
# flatten : vector로 만들어 주는 것
M = np.arange(9)
N = M.reshape((3, 3))
O = N.flatten()
print(M, '\n')
print(N, '\n')
print(O, '\n')
print(M.shape, O.shape)
'''
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8]
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]]
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8]
'''broadcasting
# 차원이 같은 경우
A = np.arange(9).reshape(3, 3)
B = 10 * np.arange(3).reshape((-1, 3))
C = A + B
A = np.arange(3).reshape((3, -1))
B = 10 * np.arange(3).reshape((-1, 3))
C = A + B
print("A: {}/{}\n{}".format(A.ndim, A.shape, A))
print("B: {}/{}\n{}\n".format(B.ndim, B.shape, B))
print("A + B: {}/{}\n{}".format(A.ndim, C.shape, C))
'''
A: 2/(3, 1)
[[0]
[1]
[2]]
B: 2/(1, 3)
[[ 0 10 20]]
'''
# (2,3,3) + (1,3,3) = (2,3,3)
A = np.arange(2*3*3).reshape((2, 3, 3))
B = 10*np.arange(3*3).reshape((1, 3, 3))
C = A + B
print("A: ", A)
print("B: ", B)
print("C: ", C)
'''
A: [[[ 0 1 2]
[ 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8]]
[[ 9 10 11]
[12 13 14]
[15 16 17]]]
B: [[[ 0 10 20]
[30 40 50]
[60 70 80]]]
C: [[[ 0 11 22]
[33 44 55]
[66 77 88]]
[[ 9 20 31]
[42 53 64]
[75 86 97]]]
'''

2차원을 3차원으로 broadcasting
def ndarray_test5():
A = np.arange(2*3*4).reshape((2, 3, 4))
B = 10*np.arange(3*4).reshape((3, 4))
C = A + B
print(C)
'''
array([[[ 0, 11, 22, 33],
[ 44, 55, 66, 77],
[ 88, 99, 110, 121]],
[[ 12, 23, 34, 45],
[ 56, 67, 78, 89],
[100, 111, 122, 133]]])
'''

+ ( 3 x 1 ) 도 ( 3 x 4 ) 로 broadcasting이 가능해서 ( 2 x 3 x 4 ) 와 broadcasting 연산 가능
ndarray indexing
def ndarray_test6():
a = np.arange(10)
print(f"ndarray: \n{a}")
# [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
print(f"a[:3]", a[:3])
# a[:3] [0 1 2]
print(f"a[::3]: ", a[::3])
# a[::3]: [0 3 6 9]
a = np.arange(9).reshape((3, 3))
print(f"ndarray: \n{a}")
# [[0 1 2]
# [3 4 5] # [6 7 8]] print(a[0][1])
# 1
a = np.arange(12).reshape((4, 3))
print(f"ndarray: \n{a}")
# [[ 0 1 2]
# [ 3 4 5] # [ 6 7 8] # [ 9 10 11]] print("a[1:3, 2]", a[1:3, 2])
# a[1:3, 2] [5 8]
💛 배운점/느낀점
- numpy로 random 추출하는 방법을 익힘, reshape 및 tensor 계산하는 방법도 익힘
- numpy broadcasting 원리를 배움
- 자습: 선형대수와 통계학으로 배우는 머신러닝 with 파이썬의 마지막 챕터 딥러닝 학습 중
- 다음 주 부터는 학원에서 머신러닝을 배울 예정
반응형
'Education > 새싹 TIL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 6주차 (수) - KNN(full code) (1) | 2023.10.11 |
|---|---|
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 6주차 (화) - KNN (1) | 2023.10.10 |
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 5주차 (목) - matplotlib (3) (0) | 2023.10.05 |
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 5주차 (수) - matplotlib (2) (0) | 2023.10.04 |
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 4주차 (금) - ML 관련 수학 (4) (0) | 2023.09.22 |