728x90
2023-09-18 16th Class
Matplotlib Basic
- ax, subplots & labels
def base_mat():
# matplotlib 기본 사용법
fig = plt.figure()
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 7))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7, 7), facecolor='linen')
ax = fig.add_subplot()
ax.plot([2, 3, 1])
ax.scatter([2, 3, 1], [2, 3, 4])
# 폰트
figsize = (7, 7)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=figsize)
# fig 제목
fig.suptitle("Title of a Figure", fontsize=30, fontfamily='monospace')
# ax 제목
ax.set_title("Title of a ax", fontsize=30, fontfamily='monospace')
# 라벨 이름
ax.set_xlabel("X label", fontsize=20)
ax.set_ylabel("Y label", fontsize=20)
fig.suptitle("Title of a Figure", fontsize=30, color='darkblue', alpha=0.9)
ax.set_xlabel("X label", fontsize=20, color='darkblue', alpha=0.7)
ax.set_ylabel("Y label", fontsize=20, color='darkblue', alpha=0.7)
fig.tight_layout()

- twinx
def my_twinx():
# twinx: 한 그래프 공간에 2개 만들기
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
ax1 = fig.add_subplot()
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
ax1.set_xlim([0, 100])
ax1.set_ylim([0, 100])
ax2.set_ylim([0, 0.1])
ax1.set_title("Twinx Graph", fontsize=30)
ax1.set_ylabel("Data1", fontsize=20)
ax2.set_ylabel("Data2", fontsize=20)
# ax1.tick_params(labelsize=20, length=10, width=3, bottom=False,
# labelbottom=False, top=True, labeltop=True, # right=True, labelright=True)
# ax1.tick_params(axis='x', labelsize=20, length=10, width=3, rotation=30) ax1.tick_params(axis='y', labelsize=20, length=10, width=3, rotation=50)
fig.tight_layout()

- text
def txt_alignment():
figsize = (7, 7)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=figsize)
ax.set_xlim([-1, 1])
ax.set_ylim([-1, 1])
ax.grid()
# labelsize 라벨 폰트
ax.tick_params(axis='both', labelsize=15)
# ax.text(x=0, y=0, s='hello', fontsize=30)
# ax.text(x=0.5, y=0, s='hello2', fontsize=30) # ax.text(x=0.5, y=-0.5, s='hello3', fontsize=30)
ax.text(x=0, y=0, va='center', ha='left', s='hello', fontsize=30)
# ax.text(x=0, y=0, va='center', ha='center', s='hello2', fontsize=30)
# ax.text(x=0, y=0, va='center', ha='right', s='hello3', fontsize=30)
def align_test():
figsize = (7, 7)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=figsize)
ax.set_xlim([-1, 1])
ax.set_ylim([-1, 1])
ax.grid()
# 'top', 'bottom', 'center', 'baseline', 'center_baseline'
# 'center', 'right', 'left' # ax.text(x=0, y=0, va='bottom', ha='right', s='Hello', fontsize=30) ax.text(x=0, y=0, va='top', ha='left', s='Hello', fontsize=30)

- ticks
def tick_mt():
# figsize = (7, 7)
figsize = (14, 7)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=figsize)
# ax.set_xlim([0, 10])
# ax.set_ylim([0, 10]) # # ax.set_xlim([0, 10]) # ax.set_xticks([0, 1, 5, 10])
# set xticks (Major and minor ticks) major_xticks = [i for i in range(0, 101, 20)]
minor_xticks = [i for i in range(0, 101, 5)]
ax.set_xticks(major_xticks)
ax.set_xticks(minor_xticks, minor=True)
ax.tick_params(axis='x', labelsize=20, length=10, width=3, rotation=30)
ax.tick_params(axis='x', which='minor', length=5, width=2)
def tick_test():
figsize = (14, 7)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=figsize)
major_xticks = [i for i in range(0, 101, 20)]
minor_xticks = [i for i in range(0, 101, 5)]
major_yticks = [i for i in range(0, 11, 2)]
minor_yticks = [i for i in range(0, 11)]
ax.set_xticks(major_xticks)
ax.set_xticks(minor_xticks, minor=True)
ax.set_yticks(major_yticks)
ax.set_yticks(minor_yticks, minor=True)
ax.tick_params(axis='x', labelsize=20, length=10, width=3, rotation=30)
ax.tick_params(axis='x', which='minor', length=5, width=2)
ax.tick_params(axis='y', labelsize=20, length=10, width=3)
ax.tick_params(axis='y', which='minor', length=5, width=2)
ax.tick_params()
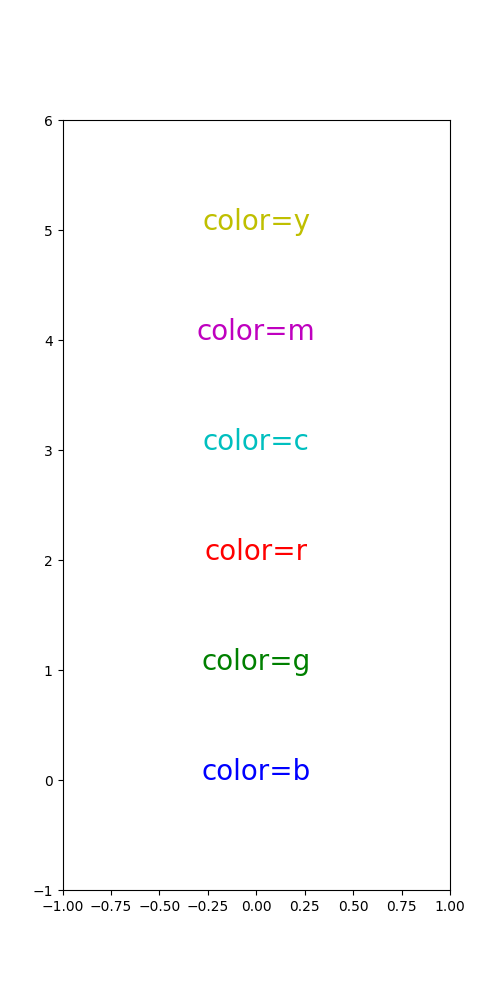
- colormat
def named_colors():
color_list = ['b', 'g', 'r', 'c', 'm', 'y']
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 10))
ax.set_xlim([-1, 1])
ax.set_ylim([-1, len(color_list)])
for c_idx, c in enumerate(color_list):
# 3번째는 텍스트임
ax.text(0, c_idx, "color="+c, fontsize=20, ha='center', color=c)
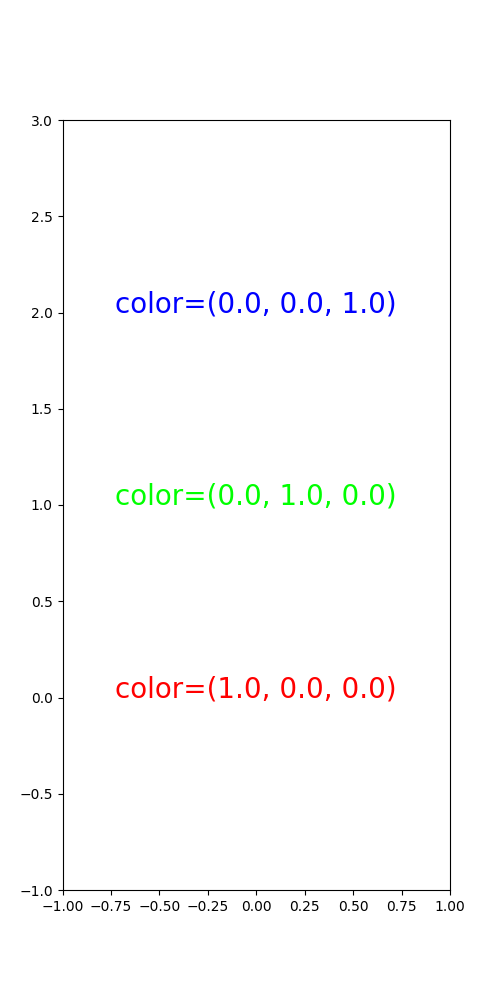
def named_colors2():
# 252, 186, 3
color_list = [(1., 0., 0.),
(0., 1., 0.),
(0., 0., 1.)]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 10))
ax.set_xlim([-1, 1])
ax.set_ylim([-1, len(color_list)])
for c_idx, c in enumerate(color_list):
ax.text(0, c_idx, f"color={c}", fontsize=20, ha='center', color=c)
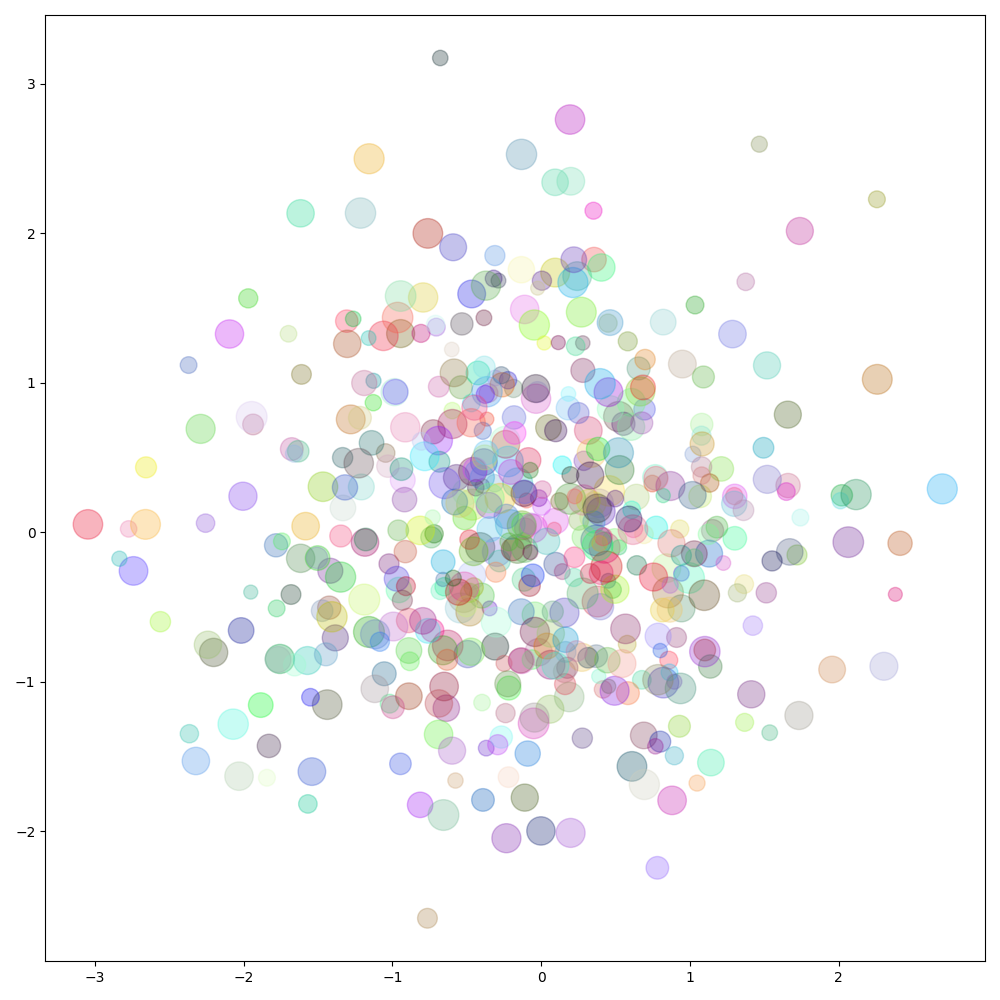
- scattor plot with random value
def my_scatter():
np.random.seed(0)
n_data = 100
# 정규분포로 랜덤값 뽑기
x_data = np.random.normal(0, 1, (n_data,))
y_data = np.random.normal(0, 1, (n_data,))
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 7))
# s는 점의 크기(marker size)
# ax.scatter(x_data, y_data, s=300, color='r')
##########################
# ax.plot(x_data, y_data, 'o', color='red', markersize=10)
# uniform linspace
# x_min, x_max = -5, 5
# n_data = 300
#
# x_data = np.random.uniform(x_min, x_max, n_data)
# y_data = x_data + 0.5*np.random.normal(0, 1, n_data)
#
# pred_x = np.linspace(x_min, x_max, 2)
# pred_y = pred_x
#
# fix, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
# ax.scatter(x_data, y_data)
#
# ax.plot(pred_x, pred_y, color='r', linewidth=3)
# size array and color array
# n_data = 10
#
# 양 옆이 정해져있고 일정하게 n_data만큼 추출
# x_data = np.linspace(0, 10, n_data)
# y_data = np.linspace(0, 10, n_data)
#
# s_arr = np.linspace(10, 500, n_data)
#
# fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
#
# s는 size라서 점점 커짐
# ax.scatter(x_data, y_data, s=s_arr)
# color array
# n_data = 10
#
# linspace 균일한 간격으로 추출
# x_data = np.linspace(0, 10, n_data)
# y_data = np.linspace(0, 10, n_data)
#
# c_arr = [(c/n_data, c/n_data, c/n_data) for c in range(n_data)]
#
# fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10)) # # s= 점 사이즈, c= 점 컬러
# ax.scatter(x_data, y_data, s=500, c=c_arr)
# size array and color array n_data = 500
x_data = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(n_data, ))
y_data = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(n_data, ))
s_arr = np.random.uniform(100, 500, n_data)
c_arr = [np.random.uniform(0, 1, 3) for _ in range(n_data)]
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
# ax.scatter(x_data, y_data, s=s_arr, c=c_arr)
ax.scatter(x_data, y_data, s=s_arr, c=c_arr, alpha=0.3)
Python (Mathmatical Algorithms Basic)
- 평균
def e109():
# mean
score1 = 10
score2 = 20
score3 = 30
n_student = 3
mean = (score1 + score2 + score3) / n_student
print(mean)
score1 += 10
score2 += 10
score3 += 10
print(score1, score2, score3)
mean = (score1 + score2 + score3) / n_student
print(mean)20.0
20 30 40
30.0- Mean subtraction
def e110():
# Mean Subtraction
# 평균 값을 구하고, 그 평균을 각 값에서 뺀 다음에 평균을 구하면 0이됨
score1 = 10
score2 = 20
score3 = 30
n_student = 3
score_mean = (score1 + score2 + score3) / n_student
score1 -= score_mean
score2 -= score_mean
score3 -= score_mean
score_mean = (score1 + score2 + score3) / n_student
print(score_mean)0.0- 분산
def e111():
# 분산
score1 = 10
score2 = 20
score3 = 30
n_student = 3
mean = (score1 + score2 + score3) / n_student
square_of_mean = mean**2
# 분산 = 편차 제곱의 평균
mean_of_square = (score1**2 + score2**2 + score3**2) / n_student
print("square of mean: ", square_of_mean)
print("mean of square: ", mean_of_square)square of mean: 400.0
mean of square: 466.6666666666667- standard deviation
def e112():
# standard deviation
score1 = 10
score2 = 20
score3 = 30
n_student = 3
score_mean = (score1 + score2 + score3) / n_student
square_of_mean = score_mean**2
# 제곱 평균
mean_of_square = (score1**2 + score2**2 + score3**2) / n_student
# 분산 = 제곱 평균 - 평균 제곱
score_variance = mean_of_square - square_of_mean
score_std = score_variance ** 0.5
# ** 0.5 루트
print("mean: ", score_mean)
print("variance: ", score_variance)
print("standard deviation: ", score_std)mean: 20.0
variance: 66.66666666666669
standard deviation: 8.16496580927726💛 배운점/느낀점
- matplotlib ax 객체 사용 방법 익힘
- 수식을 코드로 구현하는 방법을 익힘
- 내일은 파이썬으로 ML 관련 수식 코드 작성 학습 계속
반응형
'Education > 새싹 TIL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 4주차 (수) - ML 관련 수학 (2) (0) | 2023.09.20 |
|---|---|
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 4주차 (화) - ML 관련 수학 (1) (0) | 2023.09.19 |
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 3주차 (목) - visualization (0) | 2023.09.14 |
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 3주차 (수) - pandas(3), matplotlib (0) | 2023.09.14 |
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 3주차 (화) - pandas(2) (0) | 2023.09.12 |