728x90
새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 7주차 (월) - Decision Tree with Continuous Values
Continuous Descriptive Feature
#️⃣ dataset
raw (all categorical)
| ID | STREAM | SLOPE | ELEVATION | VEGETATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | FALSE | steep | high | chapparal |
| 2 | TRUE | moderate | low | riparian |
| 3 | TRUE | steep | medium | riparian |
| 4 | FALSE | steep | medium | chapparal |
| 5 | FALSE | flat | high | conifer |
| 6 | TRUE | steep | highest | conifer |
| 7 | TRUE | steep | high | chapparal |
new (Elevation이 continuous feature로 변경됨)
| ID | STREAM | SLOPE | ELEVATION | VEGETATION |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | TRUE | moderate | 300 | riparian |
| 4 | FALSE | steep | 1200 | chapparal |
| 3 | TRUE | steep | 1500 | riparian |
| 7 | TRUE | steep | 3000 | chapparal |
| 1 | FALSE | steep | 3900 | chapparal |
| 5 | FALSE | flat | 4450 | conifer |
| 6 | TRUE | steep | 5000 | conifer |
#️⃣ Continuous Descriptive (연속형 숫자)인 경우 IG 구하는 방법
- sorting values (Ascending)
- target level이 다른(Vegegation 값) 인접한 쌍 선택
- 각 subset마다 평균값을 구하고, 그 값을 선택 가능한 threshold로 세팅(추정)
- 각 threshold를 분기점으로 설정했을 때, 각각의 case에 대한 Information Gain 계산
thrreshold로 분리한 cols
full code
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
def entropy(p: list):
tot = sum(p)
p = np.array(p).astype(dtype='float64')
p /= tot
entropy = -np.sum(p * np.log2(p))
return entropy
def information_gain(parent, child):
parent_entropy = entropy(parent)
l_parent = float(sum(parent))
partition_entropy = []
for ele in child:
l_child = float(sum(ele))
part_ent = entropy(ele)
curr_ent = l_child / l_parent * part_ent
partition_entropy.append(curr_ent)
final_entropy = sum(partition_entropy)
ig = parent_entropy - final_entropy
return ig
def get_ig_idx(X, y, col_names):
ig_list = list()
parent_uniques, parent_cnts = np.unique(y, return_counts=True)
for i in range(X.shape[1]):
curr = X[:, i]
uq = np.unique(curr)
children = list()
for ele in uq:
ele_idx = (curr == ele)
curr_y = y[ele_idx]
uniq, cnts = np.unique(curr_y, return_counts=True)
# child = [[6], [1, 3]]
children.append(cnts)
e = information_gain(parent=parent_cnts, child=children)
ig_list.append(e)
ig_list = np.array(ig_list)
print("col: ", col_names)
print("gr: ", ig_list)
max_idx = np.argmax(ig_list)
return max_idx
def get_subset(X, y, max_idx, col_names):
print("==========get subset==========")
to_remain = (X[:, max_idx])
# get kind list of to_remain
uniques = np.unique(to_remain)
# split data
subset_dict = dict()
for ele in uniques:
curr_to_remain = np.array([True if x == ele else False for x in to_remain])
X1 = X[curr_to_remain]
X1 = np.delete(X1, max_idx, axis=1)
y1 = y[curr_to_remain]
subset_dict[ele] = (X1, y1)
# check if further classification is required
uq_y1 = len(np.unique(y1))
print(f"num of {ele} node: {uq_y1} {'fin' if uq_y1 == 1 else 'continue'}")
col_names.pop(max_idx)
print("="*30)
return subset_dict, col_names
def decision_tree_continuous(X, y, col_names, thresholds):
# 마지막 column만 coontinuous descriptive features인 경우의 decision tree 계산
continuous = np.array(X[:, -1], dtype=float)
categorized = None
# get T/F according to threshold
for th in thresholds:
curr_tf = (continuous <= th)
if categorized is None:
categorized = curr_tf.reshape(-1, 1)
continue
categorized = np.append(categorized, curr_tf.reshape(-1, 1), axis=1)
X_tot = np.append(X[:, :-1], categorized, axis=1)
col_names_tot = col_names[:-1] + [col_names[-1] + str(th) for th in thresholds]
''' h1 ig test '''
max_idx = get_ig_idx(X=X_tot, y=y, col_names=col_names_tot)
print(f"h1 node: idx {max_idx} {col_names_tot[max_idx]}")
# h1 node: idx 5 ELEVATION4175
# data filtration by ELEVATION4175 subset_dict, col_names = get_subset(X_tot, y, max_idx, col_names_tot)
''' h2-1(True) ig test '''
X2 = subset_dict['True'][0]
y2 = subset_dict['True'][1]
max_idx = get_ig_idx(X2, y2, col_names)
print(f"h2-1 node: idx {max_idx} {col_names[max_idx]}")
# data filtration by STREAM
subset_dict, col_names = get_subset(X2, y2, max_idx, col_names)
''' h3-1(True) ig test '''
X3 = subset_dict['True'][0]
y3 = subset_dict['True'][1]
max_idx = get_ig_idx(X3, y3, col_names)
print(f"h3-1 node: idx {max_idx} {col_names[max_idx]}")
# data filtration by ELEVATION2250
subset_dict, col_names = get_subset(X3, y3, max_idx, col_names)
def main_routine():
df = pd.read_csv('../data/vegetation_new.csv')
my_np = df.to_numpy()
data = my_np.tolist()
# print(data)
col_names = ['ID', 'STREAM', 'SLOPE', 'ELEVATION', 'VEGETATION']
data = [[2, True, 'moderate', 300, 'riparian'],
[4, False, 'steep', 1200, 'chapparal'],
[3, True, 'steep', 1500, 'riparian'],
[7, True, 'steep', 3000, 'chapparal'],
[1, False, 'steep', 3900, 'chapparal'],
[5, False, 'flat', 4450, 'conifer'],
[6, True, 'steep', 5000, 'conifer']]
data = np.array(data)
X = data[:, 1:-1]
y = data[:, -1]
threshold = [750, 1350, 2250, 4175]
print("=" * 40)
print("decision tree classification started")
print("=" * 40)
decision_tree_continuous(X, y, col_names[1:-1], threshold)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main_routine()
========================================
decision tree classification started
========================================
col: ['STREAM', 'SLOPE', 'ELEVATION750', 'ELEVATION1350', 'ELEVATION2250', 'ELEVATION4175']
gr: [0.30595849 0.57740628 0.30595849 0.18385093 0.59167278 0.86312057]
h1 node: idx 5 ELEVATION4175
==========get subset==========
num of False node: 1 fin
num of True node: 2 continue
==============================
col: ['STREAM', 'SLOPE', 'ELEVATION750', 'ELEVATION1350', 'ELEVATION2250']
gr: [0.41997309 0.32192809 0.32192809 0.01997309 0.41997309]
h2-1 node: idx 0 STREAM
==========get subset==========
num of False node: 1 fin
num of True node: 2 continue
==============================
col: ['SLOPE', 'ELEVATION750', 'ELEVATION1350', 'ELEVATION2250']
gr: [0.25162917 0.25162917 0.25162917 0.91829583]
h3-1 node: idx 3 ELEVATION2250
==========get subset==========
num of False node: 1 fin
num of True node: 1 fin
==============================
Process finished with exit code 0
decision tree picture
Continuous Target Features
target feature가 continuous한 경우는 Regression(회귀)임
따라서 Regression Decision Tree를 그려야 함
Regression Decision Tree 에서는 분기 후 subset안에서 남은 값들의 평균이 leaf node의 대표값이 됨
#️⃣ dataset
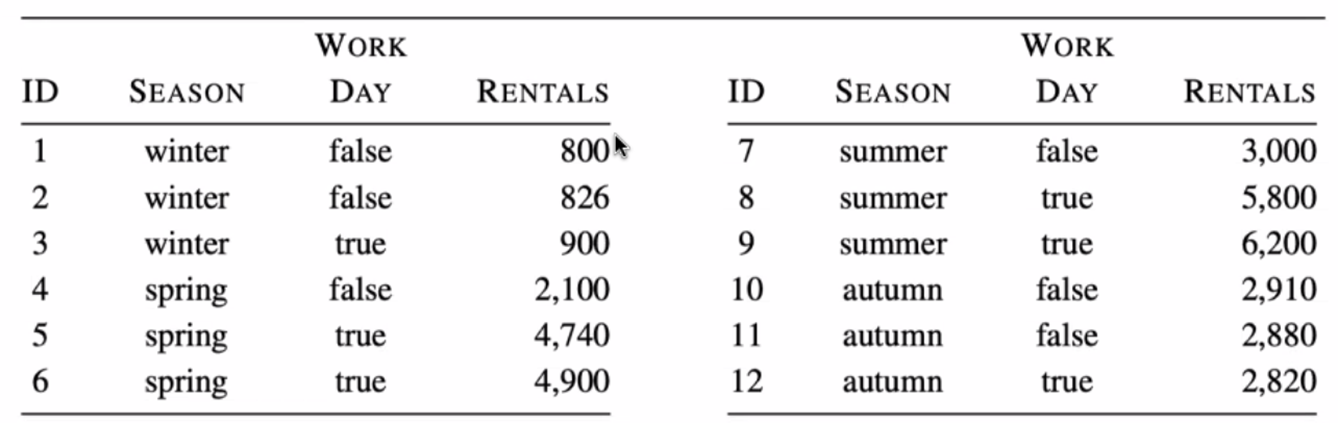
#️⃣ Continuous target (연속형 숫자)인 경우 IG 구하는 방법
- feature별로 분기를 한 후의 entropy를 구하는 대신 -> subset의 분산을 구함
- 분산의 가중평균을 summation한 값이 최종 IG가 됨
- IG가 가장 작은 경우(분산이 적게 된 경우)가 최적의 case로 간주하여 해당 feature를 해당 층의 분기용 node로 설정
full code
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
def get_variance_idx(X, y, col_names):
var_by_column_list = list()
# column 순서 대로 순회
for i in range(X.shape[1]):
x = X[:, i]
# 인덱스 종류 구하기
uniques = np.unique(x)
mean_list = list()
var_list = list()
weight_list = list()
# 인덱스 종류별로 분산 구하기
for item in uniques:
idx = np.where(x == item)
tmp = np.array(y[idx]).astype(dtype=float)
curr_mean = np.mean(tmp)
curr_var = np.var(tmp)
curr_weight = len(idx) / len(x)
mean_list.append(curr_mean)
var_list.append(curr_var)
weight_list.append(curr_weight)
# 해당 column의 가중평균을 적용한 최종 분산값 구하기
var_list = np.array(var_list)
weight_list = np.array(weight_list)
fin_val = np.sum(var_list * weight_list)
var_by_column_list.append(fin_val)
min_idx = np.argmin(var_by_column_list)
print("argmin(variance) column in current layer: ", col_names[min_idx])
return min_idx
def continuous_decision_tree():
df = pd.read_csv('../data/season.csv')
data = df.to_numpy().tolist()
# print(data)
data = [[1, 'winter', False, 800],
[2, 'winter', False, 826],
[3, 'winter', True, 900],
[4, 'spring', False, 2100],
[5, 'spring', True, 4740],
[6, 'spring', True, 4900],
[7, 'summer', False, 3000],
[8, 'summer', True, 5800],
[9, 'summer', True, 6200],
[10, 'autumn', False, 2910],
[11, 'autumn', False, 2880],
[12, 'autumn', True, 2820]]
data = np.array(data)
X = data[:, 1:-1]
y = data[:, -1]
col_names = ['SEASON', 'DAY']
min_idx = get_variance_idx(X, y, col_names)
print(f"{min_idx = }")
# SEASON
spring = np.where(X[:, 0] == "spring")
summer = np.where(X[:, 0] == "summer")
autumn = np.where(X[:, 0] == "autumn")
winter = np.where(X[:, 0] == "winter")
X_spring = X[spring, -1]
X_summer = X[summer, -1]
X_autumn = X[autumn, -1]
X_winter = X[winter, -1]
y_spring = y[spring]
y_summer = y[summer]
y_autumn = y[autumn]
y_winter = y[winter]
h1_spring_idx = get_variance_idx(X_spring, y_spring, col_names=['DAY'])
h1_summer_idx = get_variance_idx(X_summer, y_summer, col_names=['DAY'])
h1_autumn_idx = get_variance_idx(X_autumn, y_autumn, col_names=['DAY'])
h1_winter_idx = get_variance_idx(X_winter, y_winter, col_names=['DAY'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
continuous_decision_tree()
argmin(variance) column in current layer: SEASON
min_idx = 0
argmin(variance) column in current layer: DAY
argmin(variance) column in current layer: DAY
argmin(variance) column in current layer: DAY
argmin(variance) column in current layer: DAY
decision tree picture
scikit-learn으로 Decision Tree 그리기
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import tree
def iris_test():
iris = load_iris()
data, targets = iris.data, iris.target
print("data / target shape")
print(data.shape, targets.shape)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, targets, test_size=0.2, random_state=11)
print(f"{type(X_train) = } / {X_train.shape = }")
print(f"{type(X_test) = } / {X_test.shape = }")
print(f"{type(y_train) = } / {y_train.shape = }")
print(f"{type(y_test) = } / {y_test.shape = }")
model = DecisionTreeClassifier()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("depth: ", model.get_depth())
print("num of leaves: ", model.get_n_leaves())
print("--"*30)
accuracy = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print(f"{accuracy = :.4f}")
# for attr in dir(model):
# if not attr.startswith("_"): # print(attr)
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
tree.plot_tree(model, class_names=iris.target_names,
feature_names=iris.feature_names,
impurity=True,
filled=True,
rounded=True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
iris_test()
data / target shape
(150, 4) (150,)
type(X_train) = <class 'numpy.ndarray'> / X_train.shape = (120, 4)
type(X_test) = <class 'numpy.ndarray'> / X_test.shape = (30, 4)
type(y_train) = <class 'numpy.ndarray'> / y_train.shape = (120,)
type(y_test) = <class 'numpy.ndarray'> / y_test.shape = (30,)
depth: 5
num of leaves: 9
------------------------------------------------------------
accuracy = 0.8667
decision tree picture
- impurity metric은 Gini 계수를 사용
Decision Tree Mini Project
DT_1
- scikit-learn load_diabetes로 regression decision tree 그리기
- decision tree 결과분석
- regression에서 이용되는 모델학습평가지수는
(결정계수)
model.score값과 직접 계산한 R2 score 가 일치하는지 확인
full code
from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
def dt_1():
# scikit-learn load_diabetes로 regression decision tree 그리기
diabetes = load_diabetes()
data, targets = diabetes.data, diabetes.target
print("data / target shape")
print(data.shape, targets.shape)
print("="*30)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data, targets, test_size=0.1, random_state=11)
model = DecisionTreeRegressor()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 예측 및 결과 분석
preds = model.predict(X_test)
print("depth: ", model.get_depth())
print("num of leaves: ", model.get_n_leaves())
accuracy = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print(f"{accuracy = :.4f}")
r2_score = 1 - (((y_test - preds)**2).sum() / ((y_test - y_test.mean())**2).sum())
print(f"{r2_score = :.4f}")
data / target shape
(442, 10) (442,)
==============================
depth: 17
num of leaves: 391
accuracy = 0.3225
r2_score = 0.3225
DT_2
- bike_sharing.csv로 regression decision tree 그리기
- decision tree 형태와 결과 분석
full code
def dt_2():
# dataset preparation
df = pd.read_csv("../data/bike_sharing.csv")
# print(df.columns.to_list())
# ['instant', 'dteday', 'season', 'yr', 'mnth', 'hr', 'holiday', 'weekday',
# 'workingday', 'weathersit', 'temp', 'atemp', 'hum', # 'windspeed', 'casual', 'registered', 'cnt']
# selected columns out of original columns
col_names = ['season', 'mnth', 'hr', 'holiday', 'weekday',
'workingday', 'weathersit', 'temp', 'atemp',
'windspeed']
X = df[col_names].to_numpy()
y = df['cnt'].to_numpy()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
# train
model = DecisionTreeRegressor()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# predict
preds = model.predict(X_test)
# decision tree summary
print("depth: ", model.get_depth()) # depth: 32
print("num of leaves: ", model.get_n_leaves()) # num of leaves: 13351
accuracy = model.score(X_test, y_test)
print(f"{accuracy = :.4f}") # accuracy = 0.7174
depth: 32
num of leaves: 13351
accuracy = 0.7174
DT_3
- register_golf_club.csv get_entropy 함수 구현
- get_IG 함수 구현 (information Gain)
- root node에서의 descriptive feature 선정과 그 때의 I.G 값 계산
(decision tree 전체 구현 아니고, 첫번째 분기 때 이용되는 descriptive feature까지만 출력하면 됨) - 파이참으로 decision tree 그린 후, 3.의 결과와 같은지 확인
#️⃣ dataset
| Index | age | income | married | credit_score | register_golf_club |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | young | high | no | normal | no |
| 2 | young | high | no | good | no |
| 3 | middle | high | no | normal | yes |
| 4 | old | medium | no | normal | yes |
| 5 | old | low | yes | normal | yes |
| 6 | old | low | yes | good | no |
| 7 | middle | low | yes | good | yes |
| 8 | young | medium | no | normal | no |
| 9 | young | low | yes | normal | yes |
| 10 | old | medium | yes | normal | yes |
| 11 | young | medium | yes | good | yes |
| 12 | middle | medium | no | good | yes |
| 13 | middle | high | yes | normal | yes |
| 14 | old | medium | no | good | no |
full code
def entropy(p: list):
tot = sum(p)
p = np.array(p).astype(dtype='float64')
p /= tot
entropy = -np.sum(p * np.log2(p))
return entropy
def information_gain(parent, child):
parent_entropy = entropy(parent)
l_parent = float(sum(parent))
partition_entropy = []
for ele in child:
l_child = float(sum(ele))
part_ent = entropy(ele)
curr_ent = l_child / l_parent * part_ent
partition_entropy.append(curr_ent)
final_entropy = sum(partition_entropy)
ig = parent_entropy - final_entropy
return ig
def get_ig_idx(X, y, col_names):
ig_list = list()
n_unique_list = list()
parent_uniques, parent_cnts = np.unique(y, return_counts=True)
for i in range(X.shape[1]):
curr = X[:, i]
uq = np.unique(curr)
n_unique_list.append(len(uq))
children = list()
for ele in uq:
ele_idx = (curr == ele)
curr_y = y[ele_idx]
uniq, cnts = np.unique(curr_y, return_counts=True)
# child = [[6], [1, 3]]
children.append(cnts)
e = information_gain(parent=parent_cnts, child=children)
ig_list.append(e)
ig_list = np.array(ig_list)
print("col: ", col_names)
print("gr: ", ig_list)
max_idx = np.argmax(ig_list)
return max_idx, n_unique_list[max_idx]
def decision_tree_root(X, y, col_names):
max_idx, n_uniques = get_ig_idx(X=X, y=y, col_names=col_names)
print(f"h1 node: idx {max_idx}({col_names[max_idx]}), n_uniques: {n_uniques}")
return max_idx
def dt_3():
# dataset preparation
df = pd.read_csv("../data/register_golf_club.csv", index_col=0)
print(df.columns.to_list())
# ['age', 'income', 'married', 'credit_score', 'register_golf_club']
cols = df.columns.to_list()[:-1]
X = df.iloc[:, :-1]
y = df.iloc[:, -1]
max_idx = decision_tree_root(np.array(X), np.array(y), cols)
def dt_sklearn():
# 데이터 불러오기
data = pd.read_csv('../data/register_golf_club.csv')
# 특성과 타겟 분리
X = data.drop('register_golf_club', axis=1)
y = data['register_golf_club']
# # 특성에 대한 One-Hot Encoding 수행
X_encoded = X.copy()
for column in X.columns:
X_encoded[column] = X[column].astype('category').cat.codes
# 결정 트리 모델 생성
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier()
# 모델 훈련
clf.fit(X_encoded, y)
# 첫 번째 노드 (루트 노드) 정보 확인
root_node = clf.tree_
print(f"h1 node: idx {root_node.feature[0]}({X.columns[root_node.feature[0]+1]}), level:{root_node.max_depth}, threshold: {root_node.threshold[0]} ")
# 결정 트리 시각화
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
plot_tree(clf, filled=True, feature_names=X_encoded.columns, class_names=y.unique())
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# dt_1()
# dt_2()
dt_3()
dt_sklearn()
col: ['age', 'income', 'married', 'credit_score']
gr: [0.24674982 0.02922257 0.1518355 0.04812703]
h1 node: idx 0(age), n_uniques: 3 # 구현한 알고리즘
h1 node: idx 0(age), level:5, threshold: 1.5 # Scikit-Learn
반응형
'Education > 새싹 TIL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 7주차 (수) - Bayes Theorem (Multi Class & Info) (1) | 2023.10.18 |
|---|---|
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 7주차 (화) - Bayes Theorem 개념 (3) | 2023.10.17 |
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 6주차 (금) - Decision Tree with IGR (1) | 2023.10.14 |
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 6주차 (목) - Kmeans, Decision Tree 해부 (진짜열심히했음) (0) | 2023.10.12 |
| 새싹 AI데이터엔지니어 핀테커스 6주차 (수) - KNN(full code) (1) | 2023.10.11 |