Cloud Computing
1. Definition
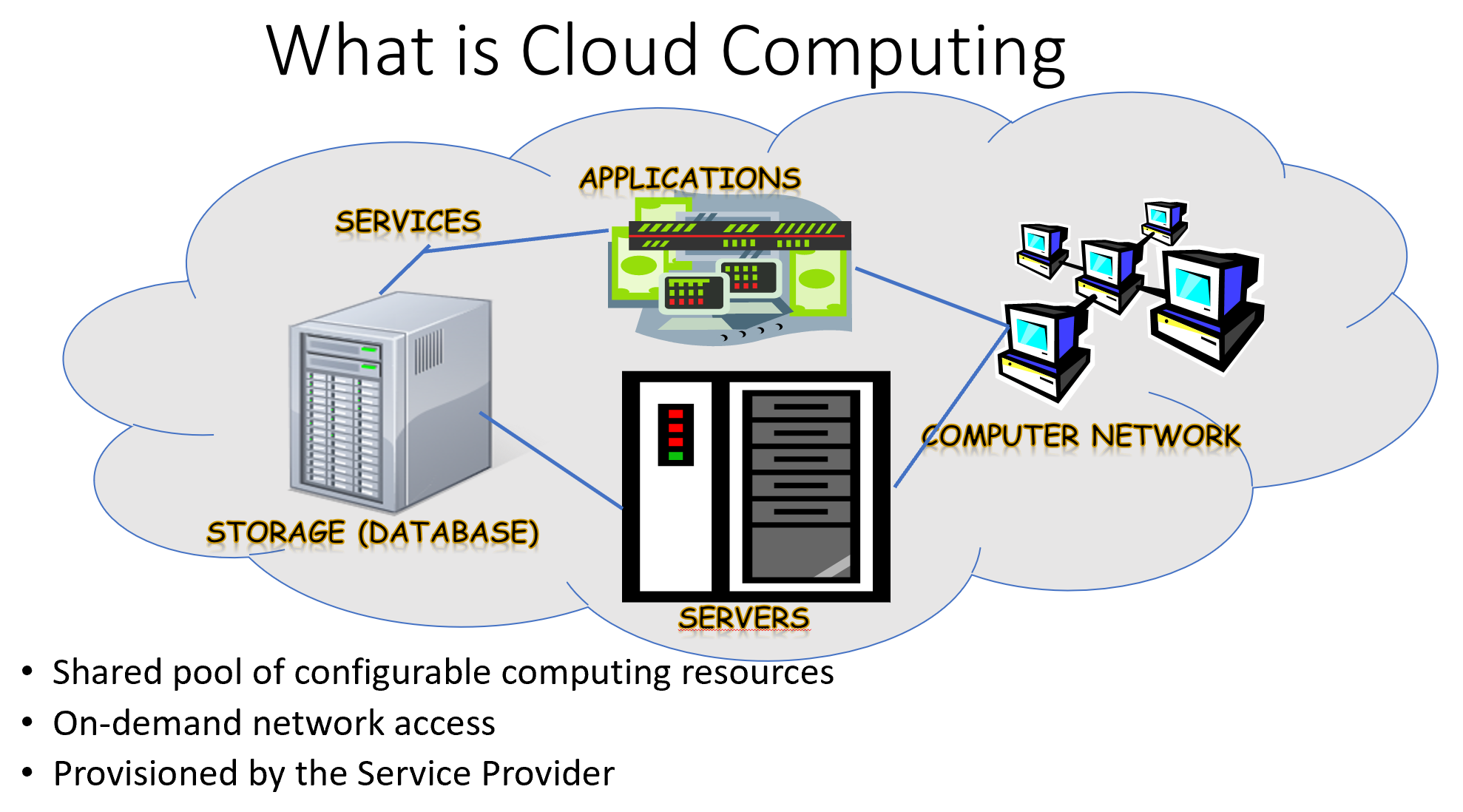
- Cloud computing is the delivery of different services through the Internet, which includes tools and applications like data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software.
- Cloud computing is a general term for anything that involves delivering hosted services over the internet.
- These services are divided into three main categories or types of cloud computing: infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and software as a service (SaaS).
- Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user.
- Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each location being a data center.
- Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and typically using a "pay-as-you-go" model which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for unaware users.

Public Cloud: Services are provided over the Internet by third-party companies. Anyone with an account can access them.
Private Cloud: Used by a single organization, often hosted on its own data center or private network.
Hybrid Cloud: Mix of public and private cloud. Provides flexibility, better optimization, and stronger security options.
Community Cloud: Shared by several organizations with common needs (e.g., same industry). Built by combining different cloud services. Managed either by a third party or by the member organizations together.
Multi-Cloud: Using multiple cloud providers at the same time. Unlike hybrid (public + private), it uses many public clouds. Increases service reliability because if one cloud fails, another is still available.
Public = open, third-party managed
Private = restricted, organization-owned
Hybrid = mix, more flexible & secure
Community Cloud = shared by organizations with similar goals
Multi-Cloud = multiple public clouds for higher reliability
2. Usage
Business tasks
- data protection
- software development
- data analylsis
- disaster recovery
- virtual desktops
- server virtualization
- customer-facing applications
Apllication examples
1) Tencent Meeting & Voov
- A cloud based video conferencing solution
- launched in 100+ countries and regions
2) Rain classroom 雨课堂
- Developed by Tsinghua Univ and XueTangX
- XueTang Cloud & teaching tool 雨课堂 (online learning)
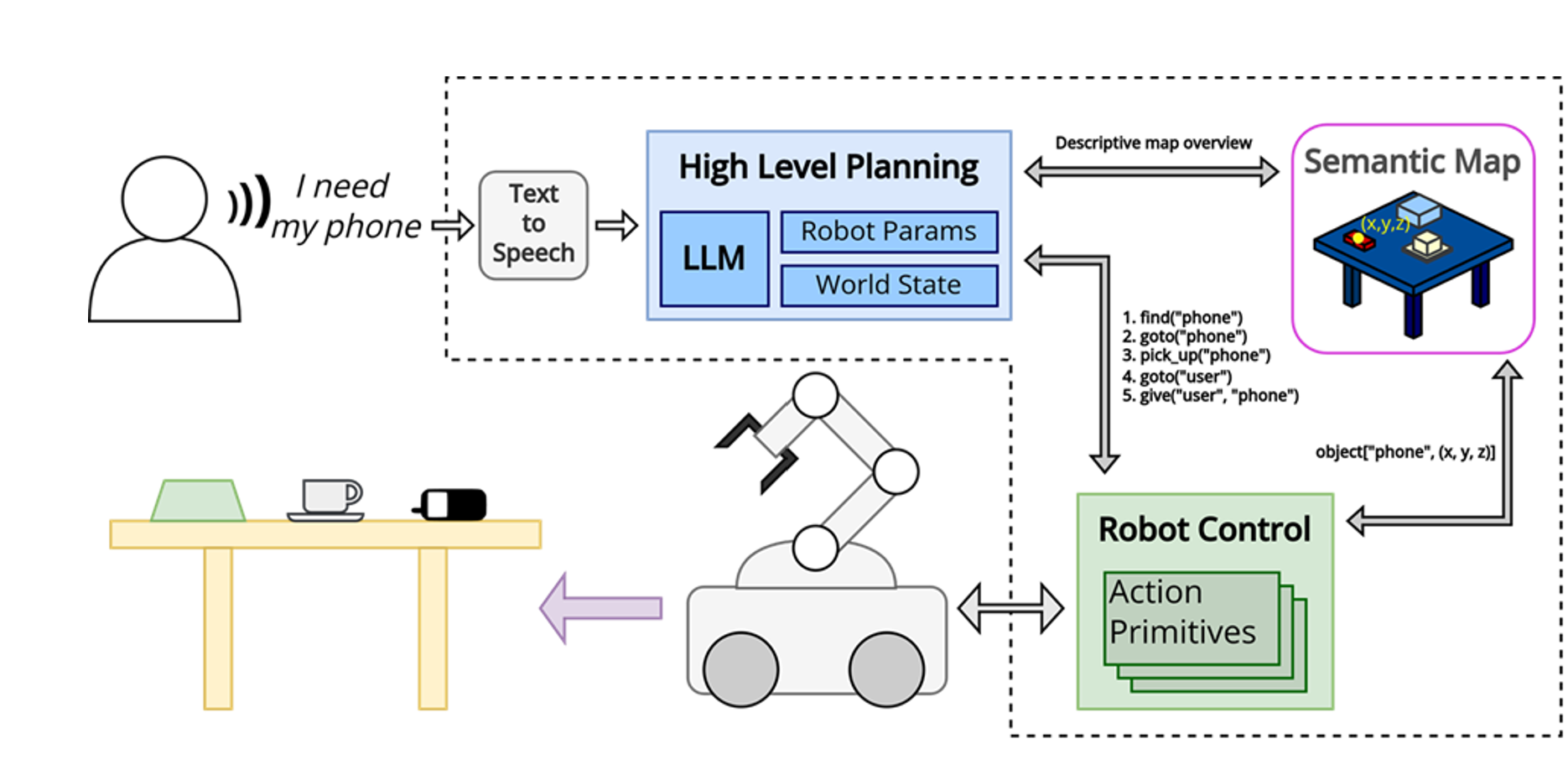
3) Cloud-based robot brain
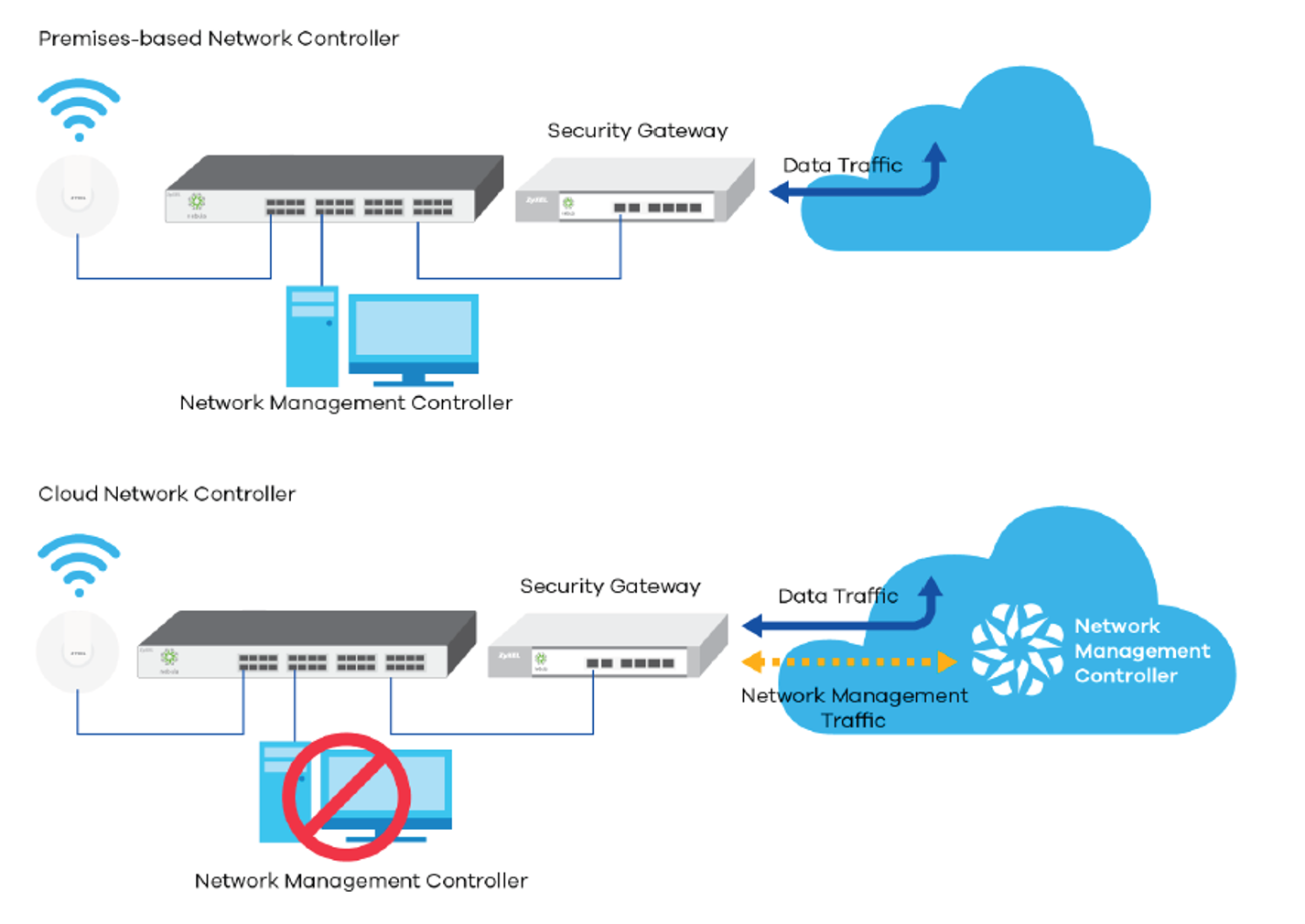
4) Cloud-based network controller
5) Big Data in the cloud
- As-a-Service pattern
- Advantages
1. improved analysis
2. simplified infrastructure
3. lowering the cost
4. security and privacy
6) NASA's Earthdata Cloud
- NASA’s Earth Science Data Systems (ESDS) Program provides open access to Earth science data, ensuring it is well-managed, accessible, and usable. The data helps researchers and decision-makers study and protect the planet.
7) Render farm in the cloud
- to render computer-generated imagery (CGI), typically for film and television visual effects.
- Fast, scalable, cost-efficient, and accessible rendering without local hardware.
8) Salesforce
- Saas Provider
- CRM
- combined AI and customer data to help sales teams identify potential leads & close sales faster
- separated clouds for customer service and marketing
3. IaaS Public Cloud Service
Amaon, Microsoft, Alibaba, Google, Huawei ..
AWS
- The largest public cloud globally
- 38.9 % of the IaaS market in 2021
- The largest profit source for Amazon
- Pay-as-you-go model: enables business to accomodate real-time shifts in data storage and usage
Alibaba 阿里云
- The largest cloud computing company in China and in Asia Pacific
- Pay-as-you-go basis
- elastic compute
- data storage
- relational databases
- big-data processing
- anti-DDoS protection
- content delivery networks (CDN)
- IaaS, PaaS, DBaaS and SaaS: managed service, web pages and aliyun commane line tools
- e-commerce
- big data
- database
- IoT
- Object Storage (OOS)
- data customization
Review
Q1. A cloud computing is a computing paradigm in which ….
Resources such as files, data, programs, hardware, and software can be accessible from a Web browser via the Internet to users
Cloud computing definition
- Cloud computing is the delivery of different services through the Internet, which includes tools and applications like data storage, servers, databases, networking, and software.
- Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user.
- Large clouds often have functions distributed over multiple locations, each location being a data center.
- Cloud computing relies on sharing of resources to achieve coherence and typically using a "pay-as-you-go" model which can help in reducing capital expenses but may also lead to unexpected operating expenses for unaware users.
Cloud Computing Characteristics

On-demand self-service
- automatically provision computing capabilities
- any type of workload on demand, server time (network storage)
- no-need-to-know -> traditional need for IT administrators to provision and manage compute resources